What is Amniocentesis?
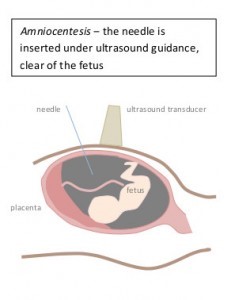
Amniocentesis is a procedure in which a fine needle is passed through the maternal abdomen and uterine wall into the amniotic fluid around the fetus in order to obtain a sample of the amniotic fluid. Cells within the amniotic fluid have the same genetic material as the fetus and can therefore be tested for genetic abnormalities such as Down syndrome.
Who is offered Amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is offered to patients who are high risk for chromosome abnormalities.
This may include:
- Abnormal first trimester screen results
- Increased nuchal translucency or other abnormal ultrasound findings
- Family history of a chromosomal abnormality or other genetic disorder
- Parents are known carriers for a genetic disorder
- Advanced maternal age (maternal age above 37).
How is it performed?
An ultrasound examination is first performed to a) confirm the dates, b) to assess the position of the placenta, and c) assess the baby for ultrasound signs of chromosomal abnormality such as Down Syndrome. The test is performed at the ultrasound clinic by an Obstetrician Gynaecologist Sonologist (specialist ultrasound doctor).
The skin of the lower abdominal wall is cleansed with an antiseptic alcohol based solution. The amniocentesis needle is then guided into the amniotic fluid by tracking its course on the ultrasound screen. It takes about 30 seconds to draw up the 20mL of straw coloured fluid required for analysis. The volume of fluid aspirated is about 1/6th of that present around the fetus and this is naturally replaced over the next 24 hours.
When is it performed?
An amniocentesis is usually performed between 15 and 18 weeks gestation. It can, however, be performed at any time throughout the remainder of the pregnancy.
What preparation is required prior to the procedure?
You will need to bring a
- Referral from your doctor
- Reports for the pregnancy (if performed elsewhere)
- Your blood group card
A moderate amount of fluid in the bladder is preferable. This can help make the uterus more accessible for the needle test.
How is the amniotic fluid analysed?
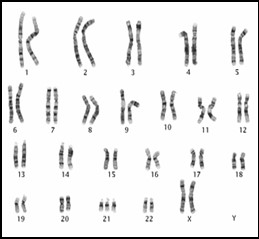
The specimen is sent to a laboratory to be processed. The fetal cells within the amniotic fluid are harvested, cultured and treated to reveal their chromosomes. Every cell should contain 23 pairs of chromosomes. The laboratory scientist examines the cells for an extra chromosome number 21 (indicating Down syndrome) and for any abnormality in the other 22 pairs of chromosomes.
In addition, each chromosome pair is stained with a special dye and examined under ultraviolet light. The individual bands of each chromosome are examined in detail for subtle genetic abnormalities such as 1) insertion of genetic material into a chromosome, 2) deletion of genetic material from a chromosome and 3) exchanging of genetic material between chromosomes (translocation). This test excludes not only Down syndrome, but a wide variety of subtle and major chromosome abnormalities.
Chromosomes indicating Down syndrome (T21)
 What is to be expected after the test?
What is to be expected after the test?
It is advisable for someone to take you home after the test and that you rest for the remainder of the day. This does not mean you should confine yourself to bed but rather you should just rest at home and avoid any strenuous activity including lifting any heavy weights.
Most patients experience a short duration of mild crampy period-like pains. This is most likely to occur after the local anaesthetic wears off, ie. within the first half hour after the test. It is safe to take paracetamol or panadol.
It is not unusual for some patients to experience slight vaginal blood spotting after the test.
If the pains worsens or spotting progresses to fresh red bleeding, then contact your doctor.
What are the risks of the test?
There is a 0.5% risk of miscarriage with the test. This is usually related to infection introduced at the time of the procedure. Antiseptic precautions are taken to minimise this risk.
Warning signs of miscarriage include strong regular period like pains with fresh red bleeding. The time when miscarriage is most likely to occur is the first 24-48 hours after the test. Contact your doctor should this occur.
How long before I know the results?
Depending on the rate of cell growth in the incubator results are available from as early as 10 up to 21 days. You will be contacted by phone with the result and a written report will also be mailed directly from the laboratory to your doctor.
Are the results accurate?
A chromosome result is one of the most reliable medical tests which has an accuracy in the order of 99.9%.


 What is to be expected after the test?
What is to be expected after the test?



